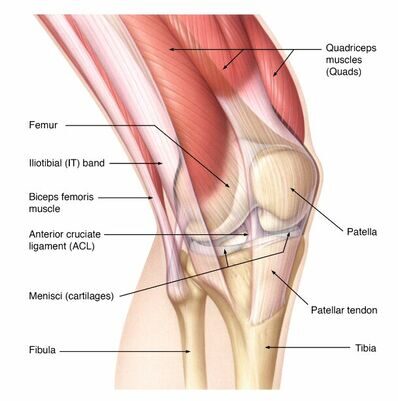
Symptoms:
The severity and location of knee pain can vary, however you should consult one of our specialists if you suffer from any of the following:
- Significant swelling and stiffness
- Redness and warmth to touch
- Instability and weakness
- Significant popping or crunching
- Inability to bend or straighten the knee
Types of Knee Pain:
- ACL Tears
- Meniscus Tears
- Knee Bursitis
- Patellar Tendinitis
- Patellofemoral Knee Pain
- Ligament Sprains
- Knee Fractures
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Septic Arthritis
Risk Factors
A number of factors can increase your risk of having knee problems. Excess weight increases stress on the knee joints during every day activities and can increase knee pain. Lack of muscle flexibility and strength can increase the risk of injuries, as the same areas of the knee will have to absorb load during tasks. Certain sports such as basketball, skiing and soccer place increased demand on the knee joint and are a factor in causing knee pain.
Prevention and Treatment
It is impossible to completely prevent knee pain, however a few strategies can prevent recurrent knee injuries.
- Gradually practice your sport or activity
- Stay strong and flexible with your lower body
- Decrease your body weight
- Be aware of past knee injuries when playing sports